
Agritech & Foodtech
- HOME
- Agritech & Foodtech

Industry-Academia-Government Collaboration Boosts Foodtech Industry in Kansai
The world faces significant challenges related to food, which sustains our lives. These include the need for increased output to meet global population growth and reducing the environmental impact of food production. As a result, the development of new technologies and the creation of innovative business models spanning the entire food value chain—from production to processing, distribution and consumption—are drawing increasing attention.
Western companies have long been leaders in the foodtech field, but in recent years, Japan has intensified its efforts to facilitate the industry's growth. In 2020, the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries led the launch of the Council for Public-Private Partnership in Food Technology. Uniting food manufacturers, startups, research institutes and relevant ministries and agencies, the council has set goals of addressing challenges and developing new markets.
During the Edo period (1603-1868), Osaka earned the title "mercantile capital of Japan," giving birth to a unique food culture, fueled by ingredients such as rice and a variety of other agricultural and fishery products from across the country. Along with Osaka, Kyoto stands as one of the most renowned centers of "washoku" Japanese cuisine, recognized as a UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage. The Kansai region, with its deep historical and cultural ties to food, is home to universities with agricultural departments, research institutes focused on agriculture, and food manufacturers. A growing number of foodtech companies, including startups emerging from universities, are making their mark in the industry.
Other local governments in the Kansai region are also actively working to foster the foodtech industry. For example, the Kyoto Foodtech Basic Concept, developed by the prefecture, brings together a cluster of related companies, supports R&D efforts, and facilitates collaboration between universities and businesses.
This section highlights a selection of businesses driving innovation in the agritech and foodtech industries. We invite you to visit these companies and experience their cutting-edge innovations.



COMPANY LIST Listings:8

Agritech-plus Co., Ltd.
Nara Prefecture
161-2 Ajima, Tawaramoto-cho, Shiki, Nara Prefecture, 636-0245
Agritech & Foodtech
Agritech-plus Co., Ltd. Nara Prefecture https://agritech-plus.jp/
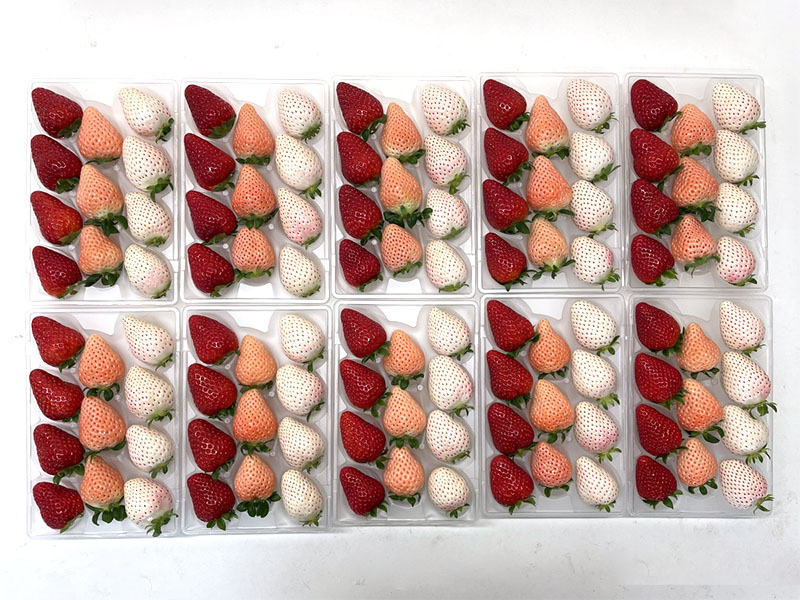
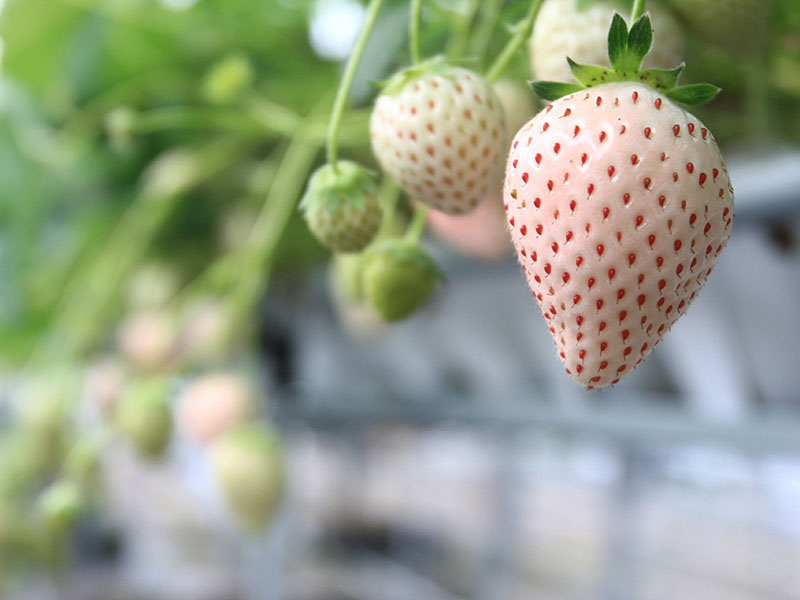



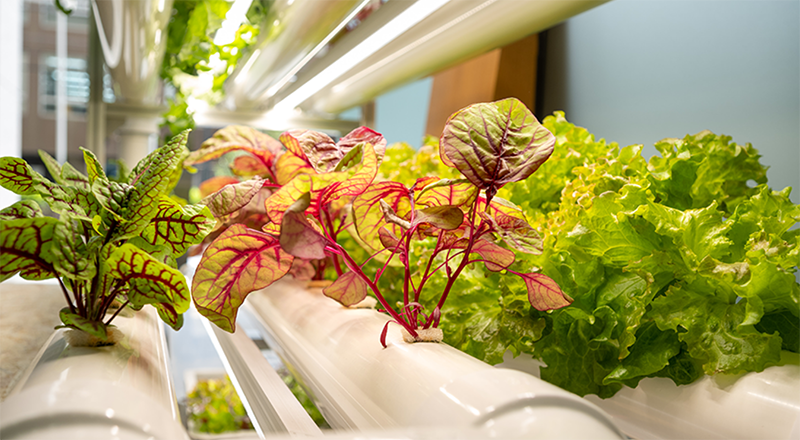
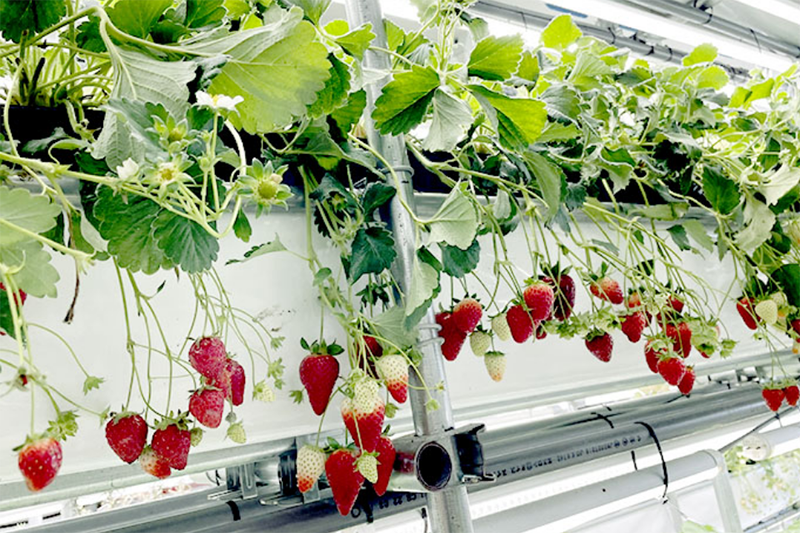
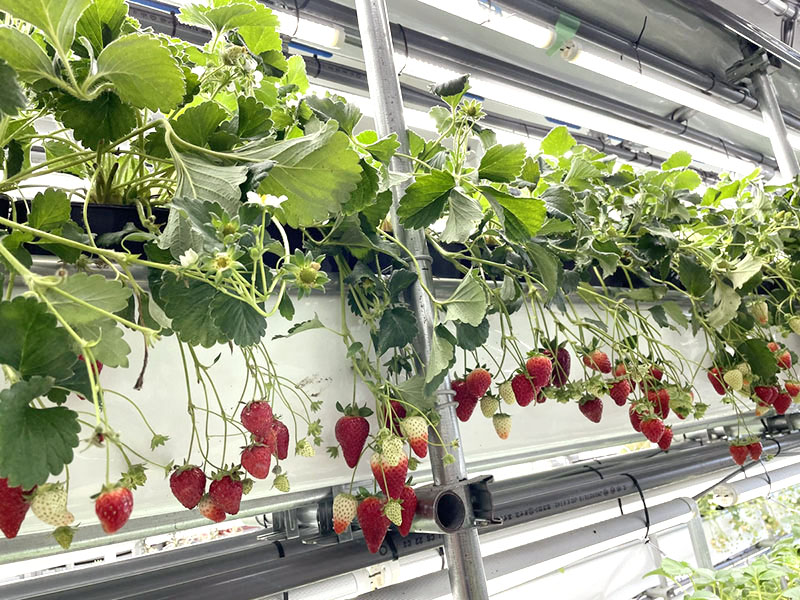
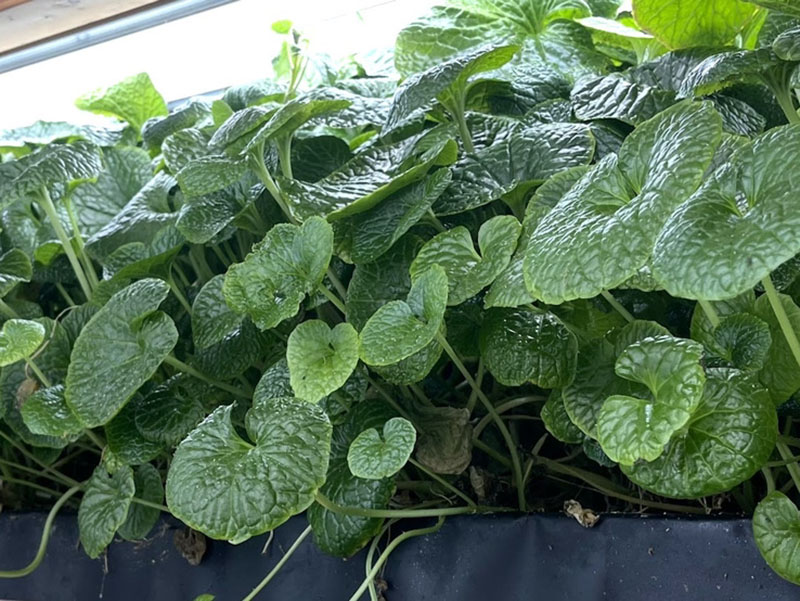
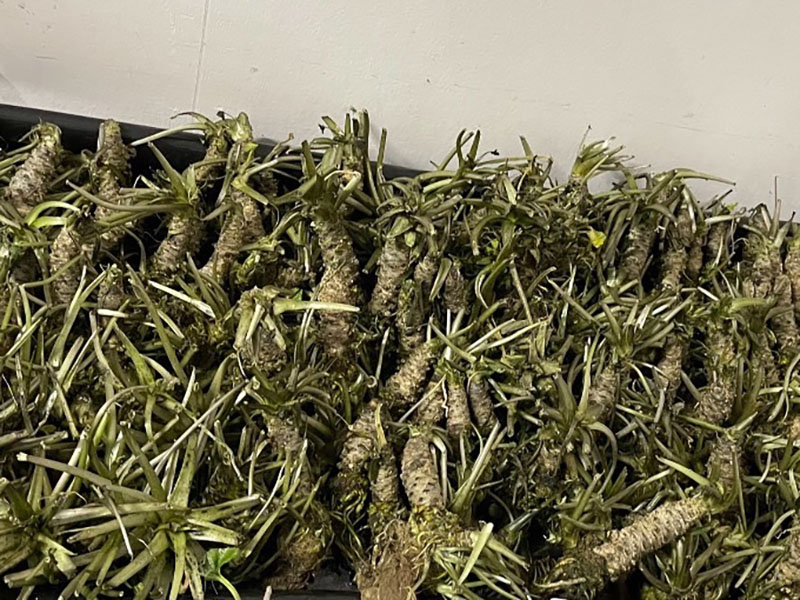
Agritech-plus Co., Ltd. works to achieve sustainable agriculture by providing solutions to challenges related to agriculture. As a means to resolve such issues, including falls in food self-sufficiency, the agricultural population and cultivation areas, the company is developing plant factories - one using sunlight, and the other using solar and artificial light together. With the sunlight type, Agritech-plus has succeeded for the first time in the world in the year-round production of strawberries that usually bear fruit once in a year, employing dark control technology. Using the solar-artificial light hybrid type, the company has succeeded in the year-round production of strawberries and the production of a wide variety of crops including wasabi, leafy vegetables, medicinal plants and herbs. The hybrid type, which uses ready-made agricultural equipment, costs less than half of a conventional plant factory to build. The company's factories use its dense planting technology to produce more than conventional vertical plant factories.


Tour Location
About 1 hour's drive from Osaka International Airport (Itami Airport)
About 20 minutes' drive from Yamato-Yagi Station on Kintetsu Railway's Osaka Line and Kashihara Line
Availability of Company Tours
Contact Information
CEO

KYOEISEICHA CO., LTD.
Kyoto Prefecture
8-1-2 Umemidai, Kizugawa, Kyoto Prefecture 619-0215

Agritech & Foodtech
KYOEISEICHA CO., LTD. Kyoto Prefecture https://www.kyoeiseicha.co.jp/
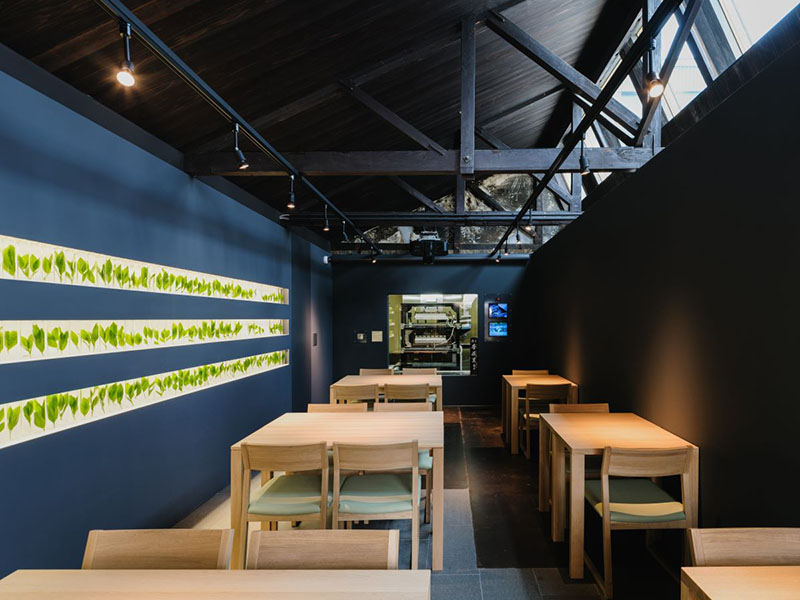



Kyoeiseicha Co., Ltd. is engaged in tea production, focusing on high-quality Japanese teas, with its base in Kyoto Prefecture.
Since its establishment in 1836, the company has been rated highly both in Japan and overseas for fusing traditional production methods with the latest technologies. It uses tea leaves carefully selected by leading tea masters and produces tea under a strict quality management system at FSSC22000 certified facilities, meeting diverse needs ranging from commercial-use teas to high-quality products.
Kyoeiseicha has also been certified for compliance with Halal and Kosher requirements. Its "macha" green tea boasts a top-class production volume and is sold not only in Japan but also exported to more than 30 countries in North America, Europe, Asia and Oceania, playing a key role in spreading Japanese tea culture around the world. The company also focuses on OEM operations and conducts consignment production under customer brands, contributing to the business development of partner companies.
While aiming to establish a sustainable business system centered on environmental conservation, Kyoeiseicha also actively carries out research on the health benefits of matcha. The company aims to continue its contributions to the development of local communities and the industry by pursuing "trusted quality."
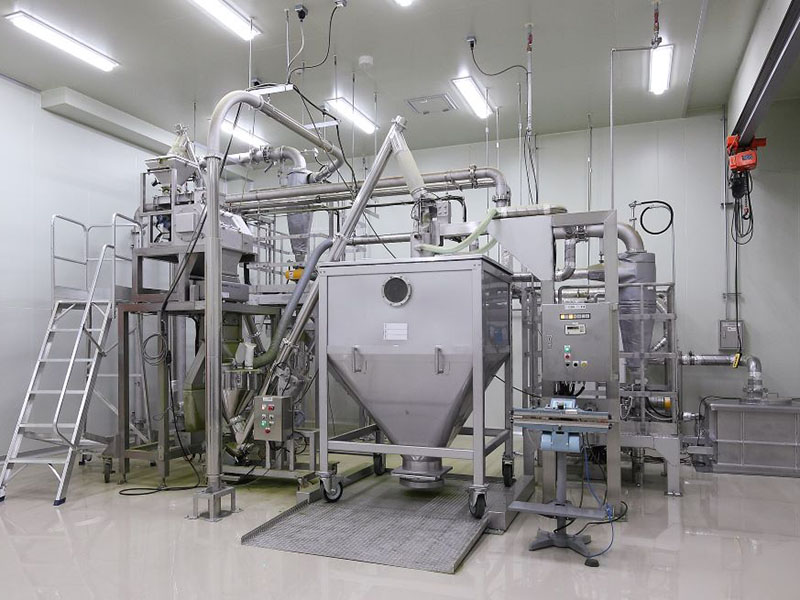


Tour Location
8-1-2 Umemidai, Kizugawa, Kyoto Prefecture 619-0215
About one hour's drive from Shin-Osaka Station
Availability of Company Tours
Contact Information
Global Business Division
Special Note
In addition to the above-mentioned Kyoto Techno Center (the manufacturing and development base), TEA SQUARE MORIHAN, a Japanese tea culture facility in Uji, Kyoto Prefecture, is also open for tours.
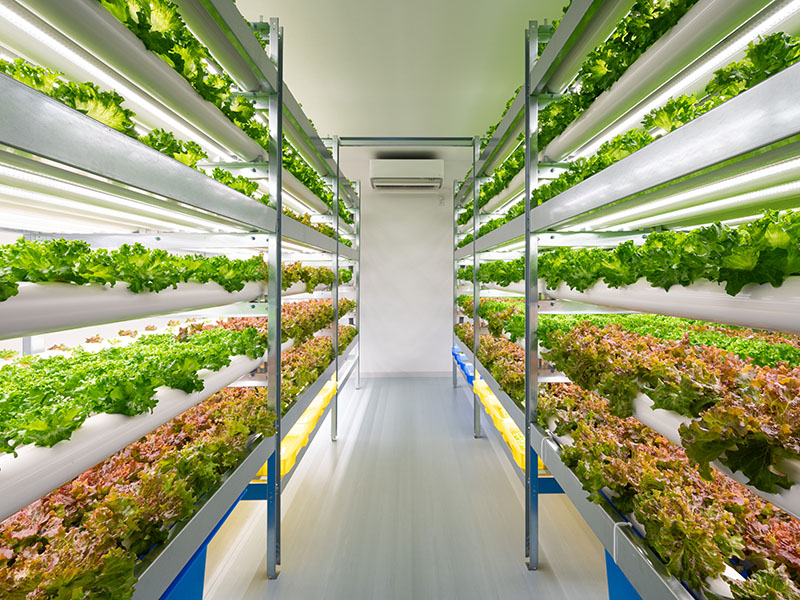

spicecube.inc
City of Osaka
1-1-30 Sakuragawa, Naniwa Ward, Osaka,Osaka Prefecture 556-0022

Agritech & Foodtech
spicecube.inc City of Osaka https://www.spicecube.biz/
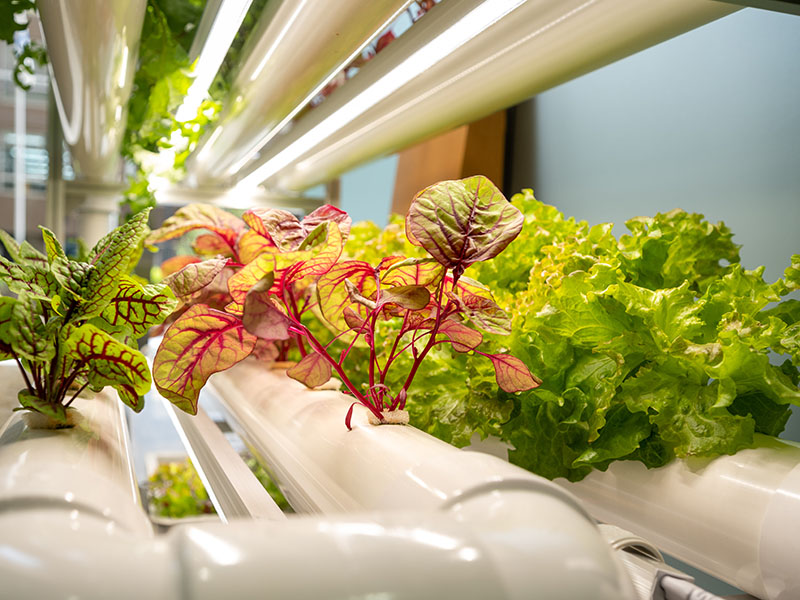



As an agri-tech startup, spicecube.inc specializes in plant factories. Indoor agriculture, which does not require farmland, can solve many challenges, including low food self-sufficiency caused by the declining agricultural population, and spicecube.'s business model is not just building plant factories but also support the distribution of related products. The company can help farmers distribute products at their desired prices, which it thinks is most important for agricultural businesses. It is developing a system that allows indoor vegetables to absorb carbon dioxide emitted from offices and homes, while believing that indoor farming can also contribute to reducing carbon dioxide emissions by using LED lighting and cultivation technology that circulates nutrient solution.
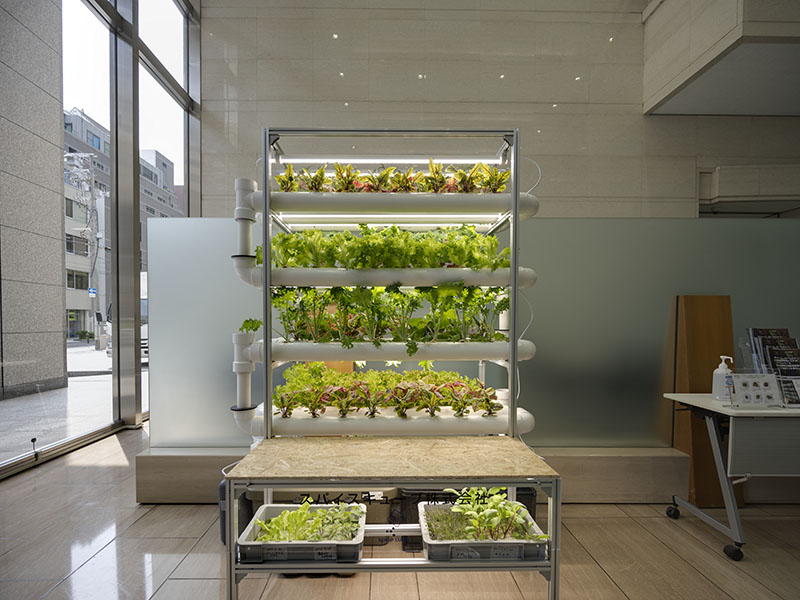
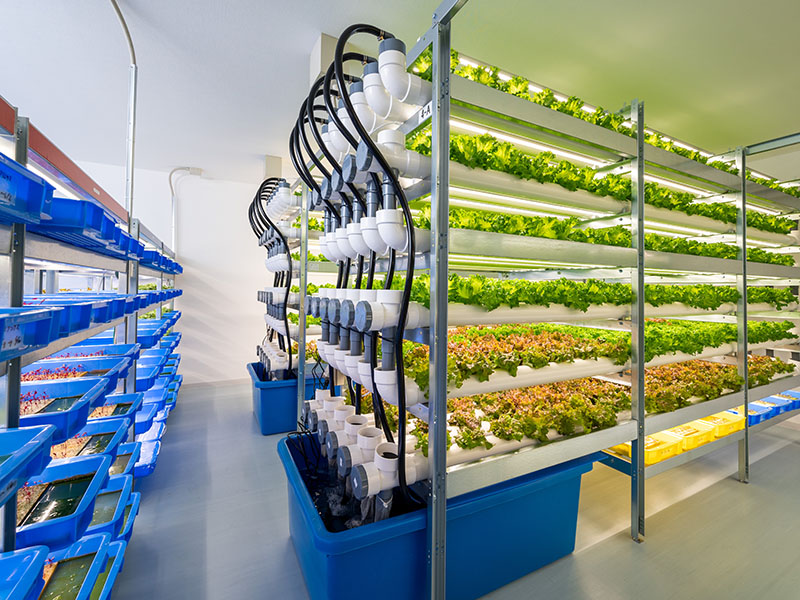


Tour Location
About 30 minutes' drive from Osaka International Airport (Itami Airport)
Availability of Company Tours
Contact Information
Representative Director

tashimaboring, Ltd
Tottori Prefecture
2-8-15 Yoshinariminami-machi, Tottori, Tottori Prefecture, 680-0871

Agritech & Foodtech
tashimaboring, Ltd Tottori Prefecture https://tashima-boring.com/
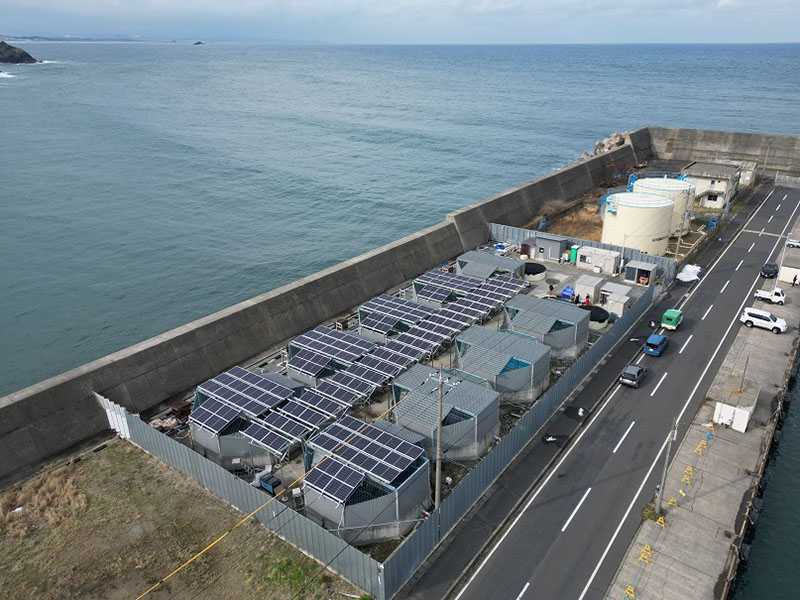
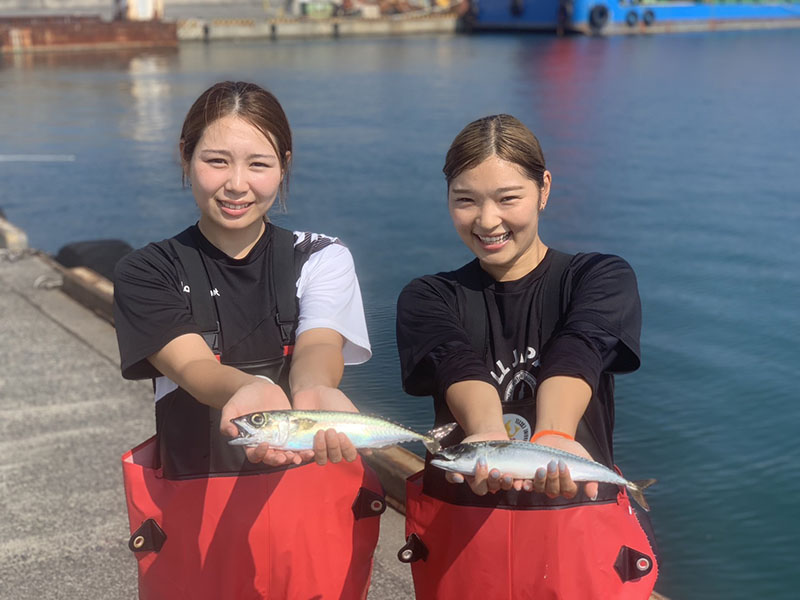



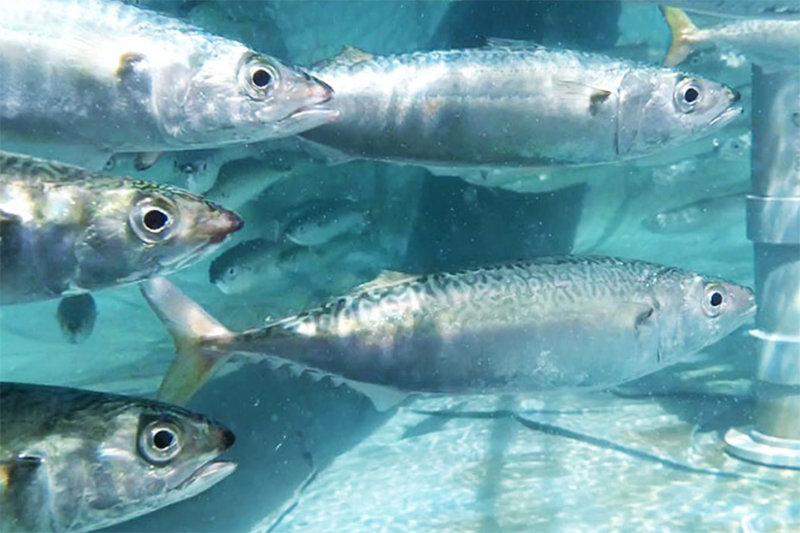
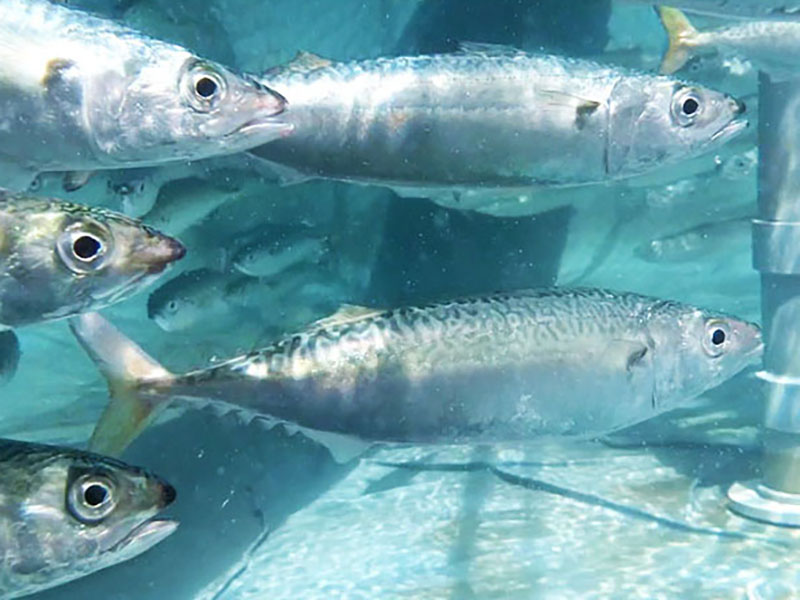
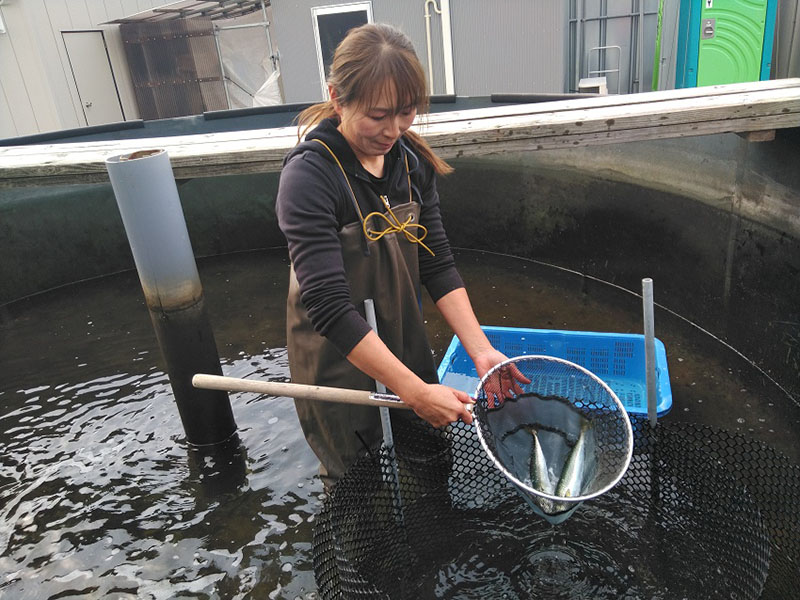
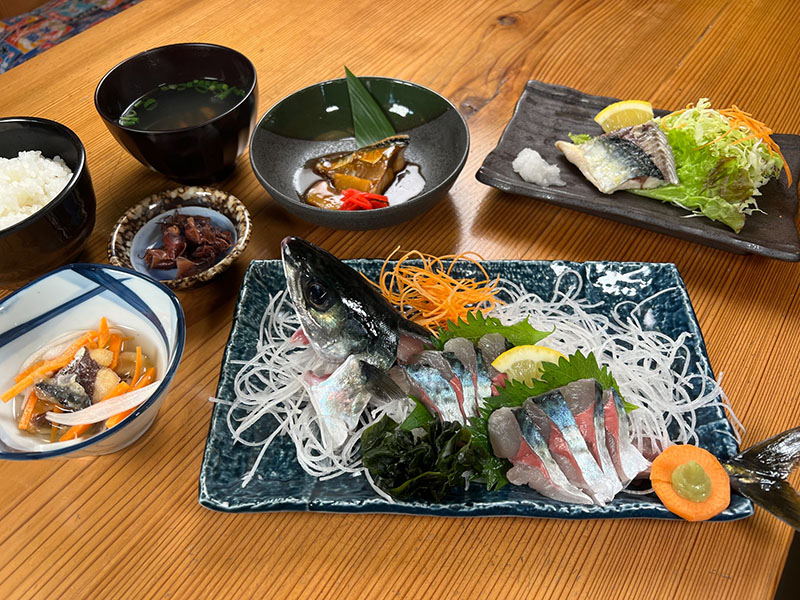
Since its founding in 1986, tashimaboring, Ltd. has been engaged in well drilling across Japan. In April 2021, the company launched land-based mackerel farming using underground seawater. Amid declining catches due to changes in the marine environment, the company believed that land-based aquafarming has the potential for sustainable catches. The company is working to build a business model that seeks to develop a sustainable fishery industry, by using its well drilling technology while utilizing natural energy such as solar power.


Tour Location
Availability of Company Tours
Contact Information
Land-Based Aquaculture Business Department
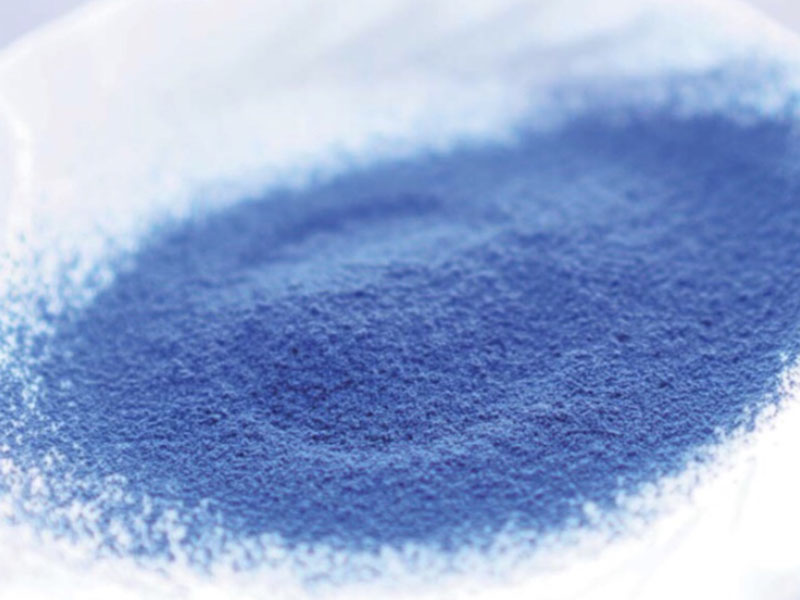

Tsujiko Co., Ltd.
Shiga Prefecture
1750-1 Kitawaki, Minakuchi-cho, Koka, Shiga Prefecture, 528-0057

Agritech & Foodtech
Tsujiko Co., Ltd. Shiga Prefecture http://www.tsujiko.com/en/



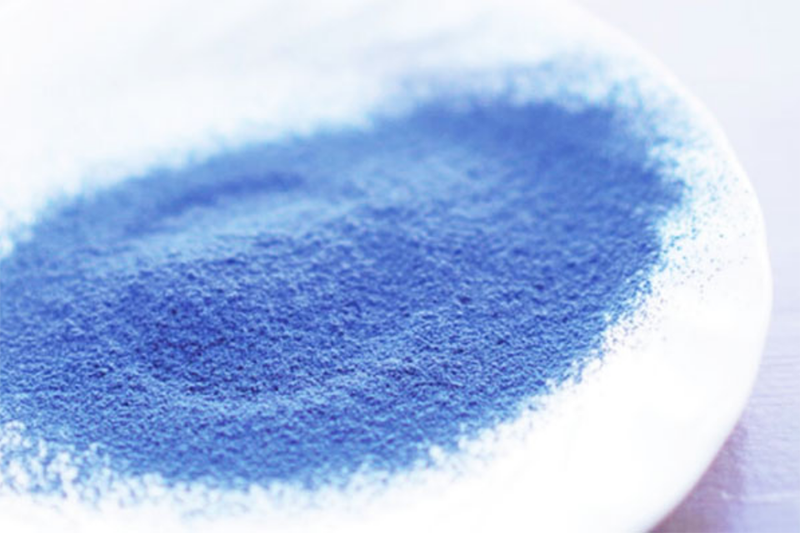
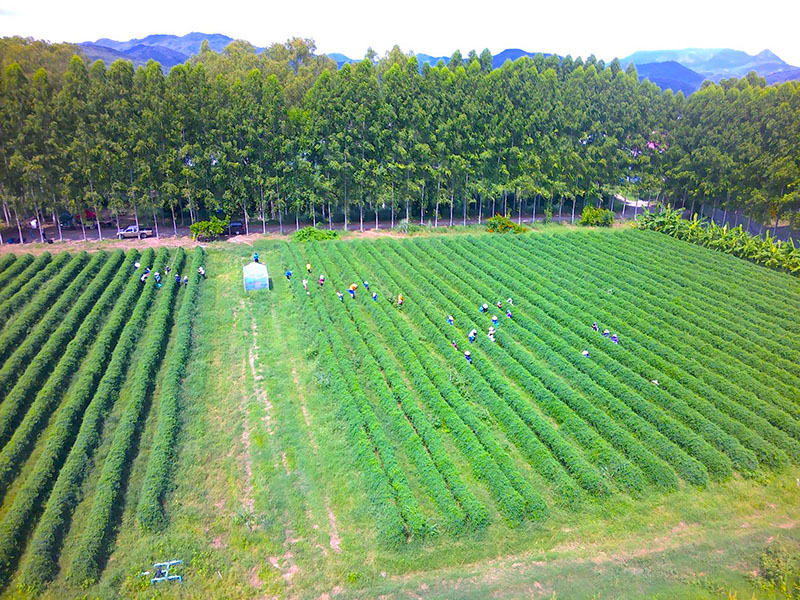
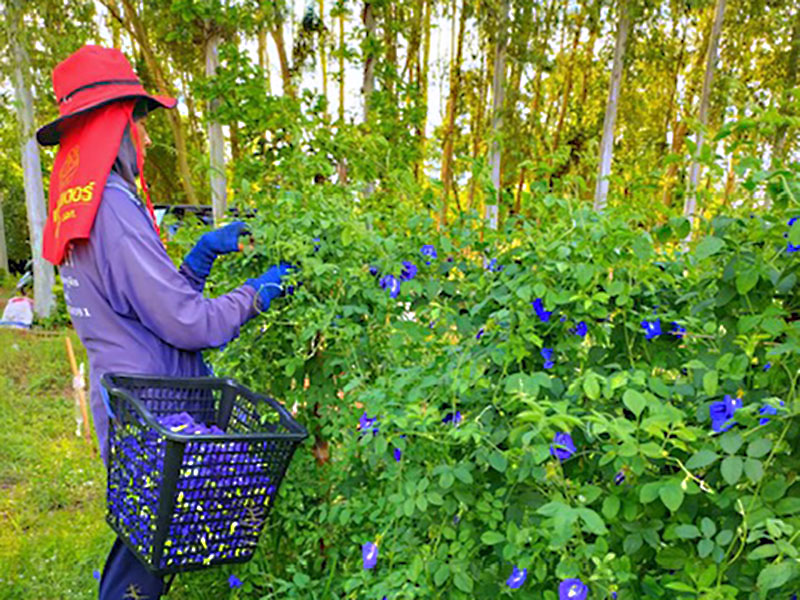
Founded in Koka, Shiga Prefecture, in 1963, Tsujiko Co., Ltd. designs and manufactures lighting equipment. The company is also active in mechatronics, for the design and assembly of factory automation systems; outsourcing related to auto parts production; natural food raw materials operations; and the small-lot processing of vegetables and fruit. At a plant in Phetchabun, Thailand, Tsujiko processes butterfly pea petals into blue natural powder for food coloring. The company's processing technology is characterized by an ability to sterilize and pulverize plants without losing their nutritional value.


Tour Location
Availability of Company Tours
Contact Information
Yasu Office
Special Note
The tour provides visitors with a chance to look at natural food production for food coloring.
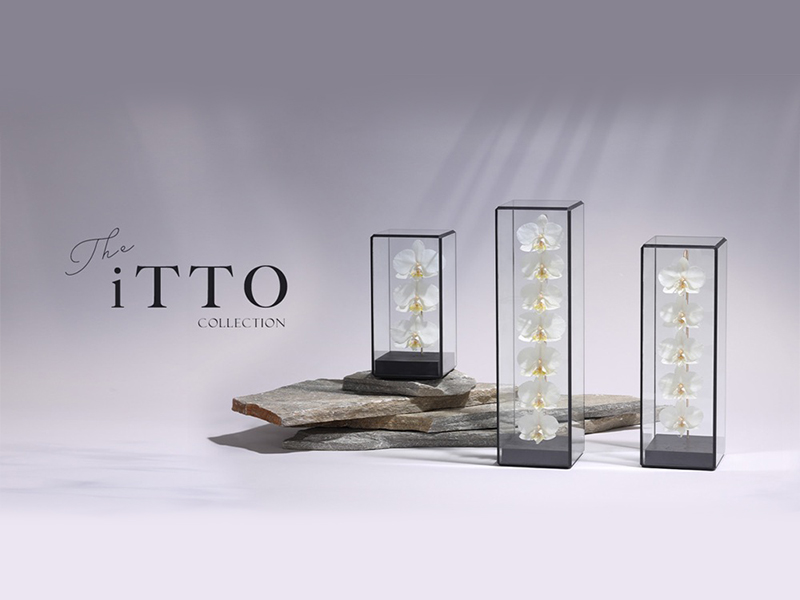

Hongo Industry Co.
Shiga Prefecture
Blezio 9, 4th Floor 1-6-18 Ogaya, Osu, Shiga Prefecture 520-2144

Agritech & Foodtech
Hongo Industry Co. Shiga Prefecture https://www.hongou-i.jp/business/smart_agriculture/



Headquartered in the city of Otsu, Shiga Prefecture, Hongo Industry Co. has been deeply rooted in the local community since it was established in 1996. It operates a diverse range of businesses, with a primary focus on circular civil engineering and construction, along with environmentally sustainable projects. In addition to conventional public works and residential land development projects, the company is committed to sustainable practices, promoting circular construction by utilizing recycled materials.
It is active in the renewable energy sector, developing a proprietary energy storage system designed to support local energy production and consumption, while also enhancing disaster response capabilities.
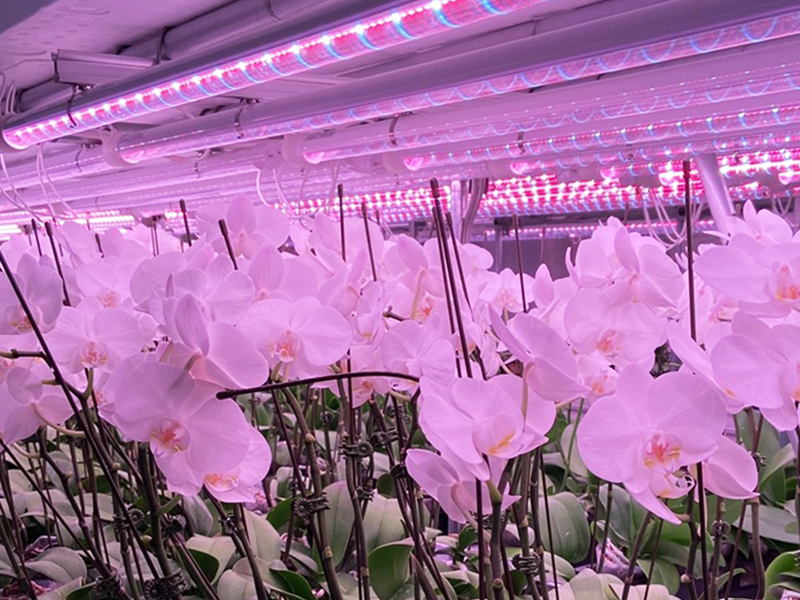
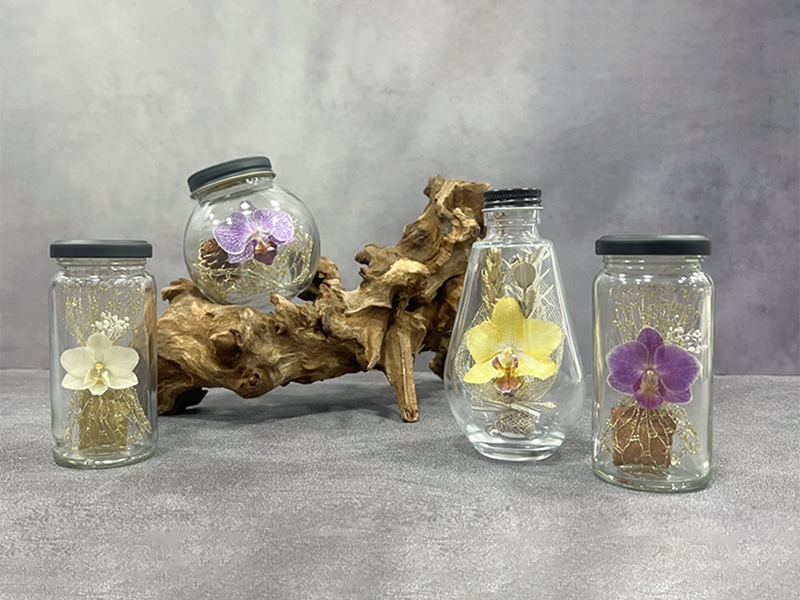
In recent years, Hongo Industry has expanded into smart agriculture, cultivating Phalaenopsis orchids in state-of-the-art facilities equipped with LED lighting and proprietary energy storage technology. The company has also commercialized its patented "natural dried flowers" from a unique in-house process, launching the "iTTO GINZA" brand to offer related products as gifts and for interior decor. By integrating renewable energy and local resources, Hongo Industry is committed to fostering a more sustainable society.
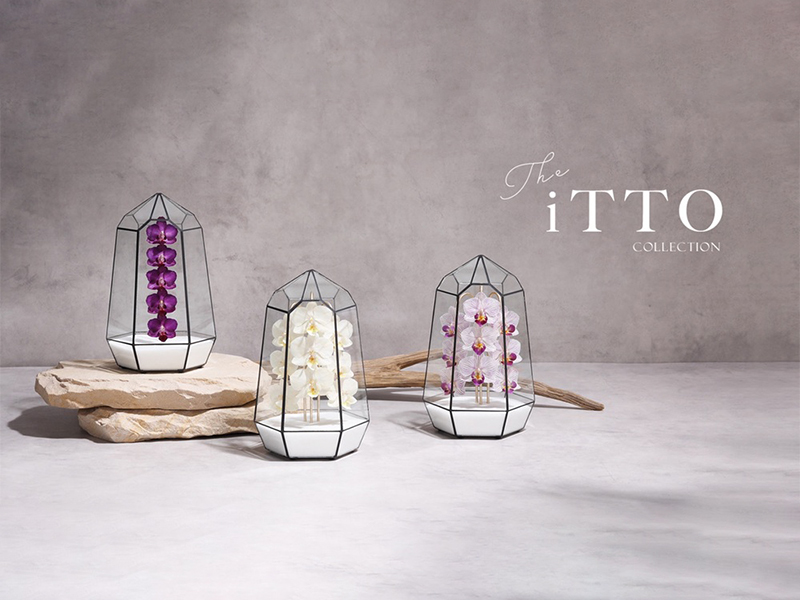
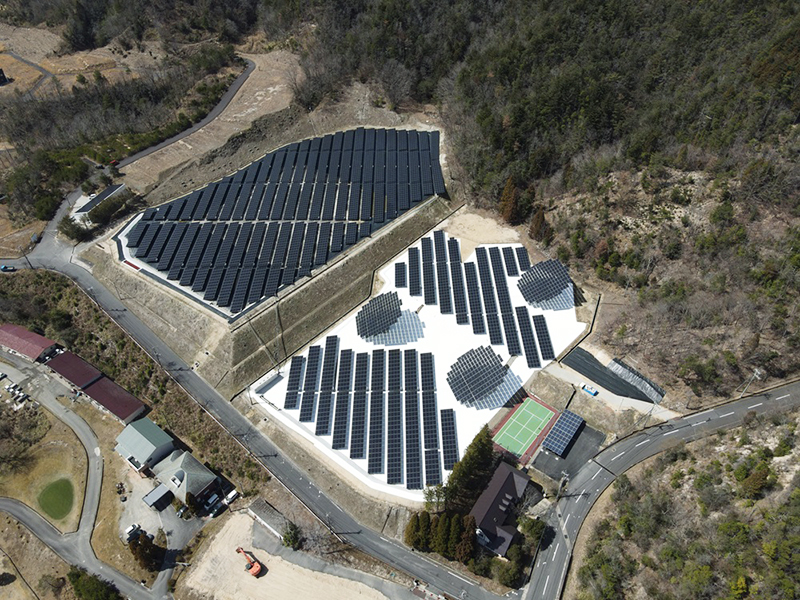


Tour Location
At Kusatsu Station on the JR Biwako Line, transfer to the JR Kusatsu Line and ride to Kibukawa Station. At Kibukawa, transfer to the Shigaraki Kohgen Railway and travel to Shigarakigushi Station.(about 24 minutes)
Availability of Company Tours
Contact Information
Agribusiness Department Head Office

NINZIA Inc.
Kobe
KiP, 56 Naniwa-machi, Chuo Ward, Kobe, Hyogo Prefecture 650-0035

Agritech & Foodtech
NINZIA Inc. Kobe https://ninzia.jp/en/
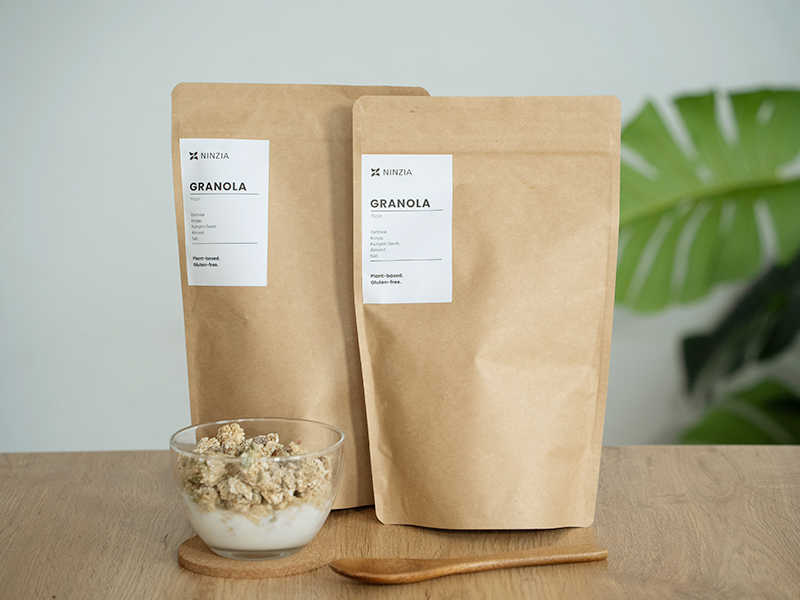



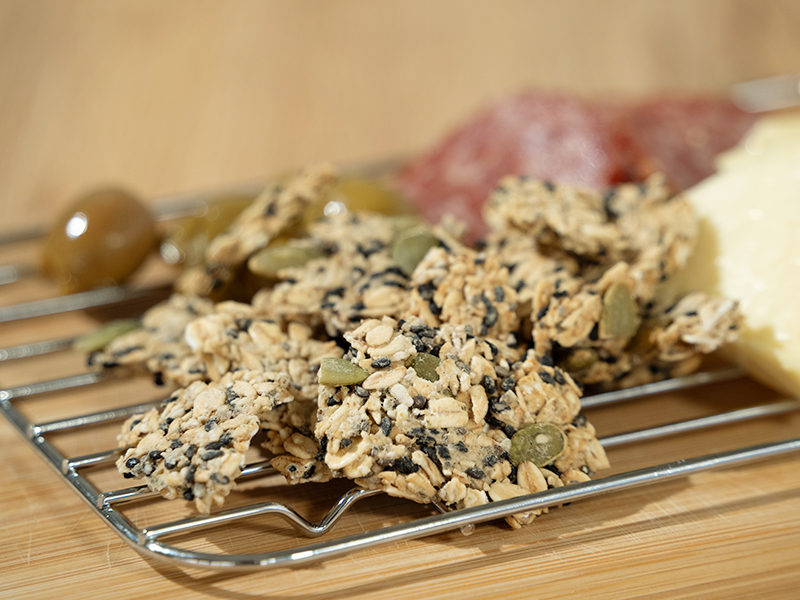
NINZIA Inc. developed its "NINZIA PASTE" ingredient using dietary fibers from konjac, a traditional Japanese food. This proprietary product can be employed to make a variety of foods without the use of gluten, sugar, oil or eggs. Research shows reductions in blood glucose spikes.
The company provides products and technologies that meet a variety of dietary needs, including plant-based, allergen-free and halal-friendly, for a world in which people are free to enjoy eating.
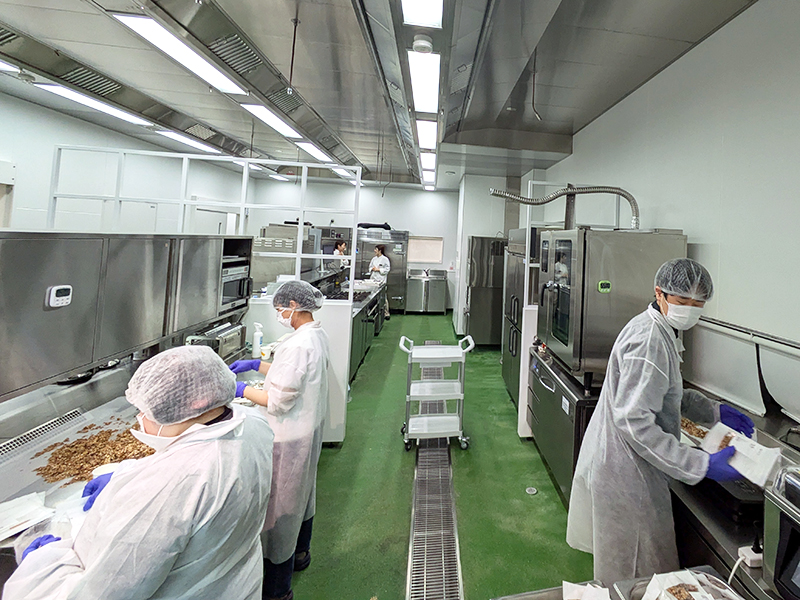


Tour Location
MILAB, Galilei Group Headquarters Building, 2-6-18 Takeshima, Nishiyodogawa Ward, Osaka, Osaka Prefecture 555-0011
Availability of Company Tours
Contact Information
Representative President
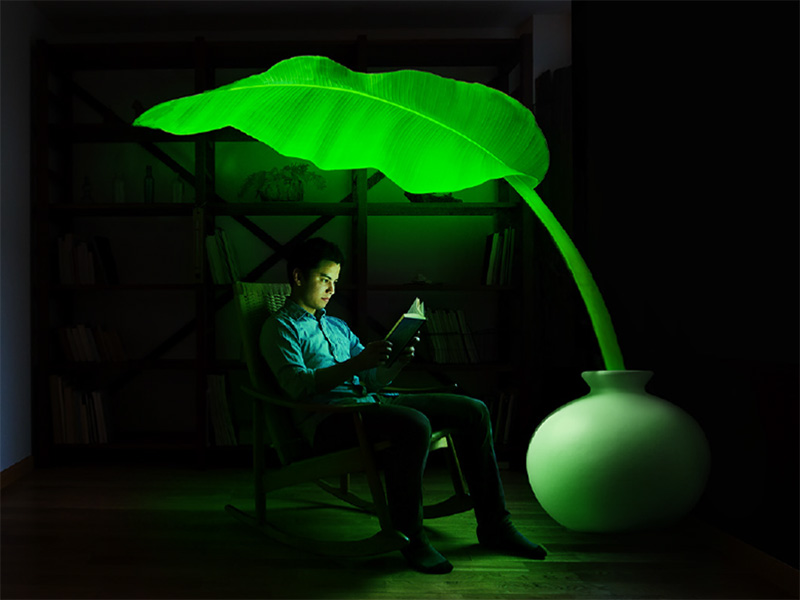

LEP Inc.
City of Osaka
1-1-3-267, Umeda, Kita Ward, Osaka, Osaka Prefecture 530-0001

Agritech & Foodtech
LEP Inc. City of Osaka https://www.start-lep.jp/en/home-2/
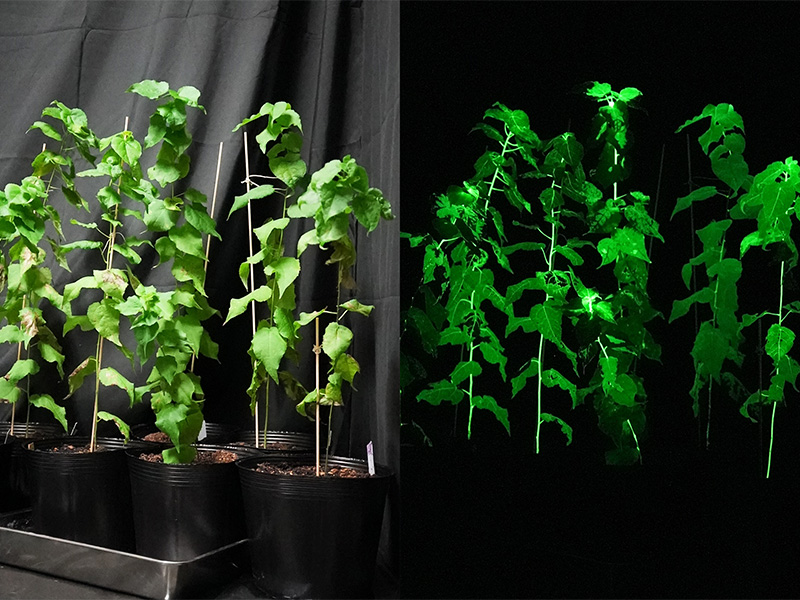
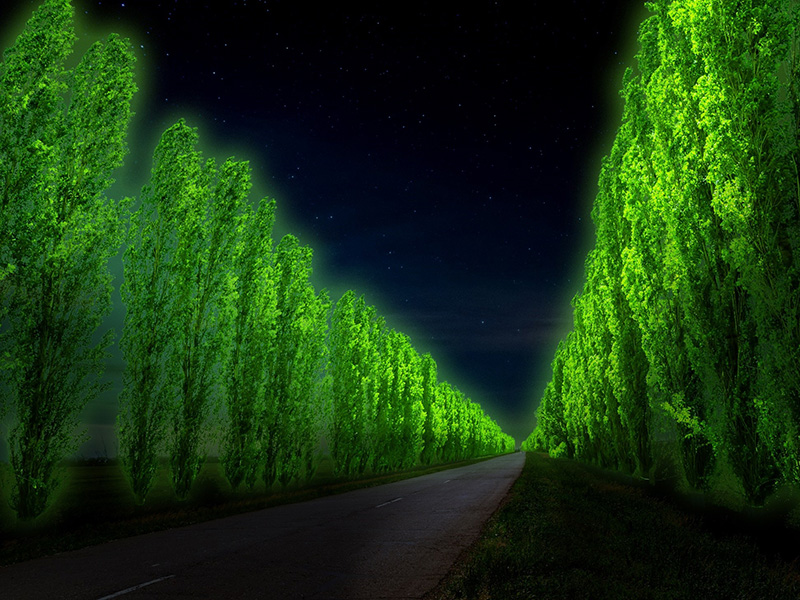



Inspired by luminous organisms in nature, such as fireflies and mushrooms, LEP Inc. is conducting research and development on plants that have “bright luminescent proteins.” We aim to develop “light emitting flowers” and “light emitting ornamental plants” for use as interior accessories, as well as “light emitting roadside trees” that can replace street lights. If realized, such “light emitting plants” will absorb CO₂ through photosynthesis during the daytime, and at night light rooms and streets, like conventional illumination but without the use of electricity. They could be the ultimate eco-friendly lighting and therefore a critical key to resolving global warming and energy-related issues.


Tour Location
Nara Institute of Science and Technology Labo C615 8916-5 Takayama-cho, Ikoma, Nara Prefecture
Nara Institute of Science and Technology Labo: An hourlong drive from Osaka International Airport (Itami Airport),An hourlong drive from Kyoto Station
Availability of Company Tours
Contact Information
Executive Officer